The connection between oxygen and weight loss has sparked curiosity among fitness enthusiasts and researchers alike.
Did you know that up to 75% of your daily calorie burn is just for basic body functions like breathing?
It's not hard to figure out what happens when you exercise and breathe better…you lose weight faster.
We don't mean breathing exercises but actual workouts.
At BELDT Labs, we researched oxygen's role in weight management and natural compounds that offer respiratory support to enhance our now best-selling fat burner, SKALD.
In this article, we'll share what we've learned in simple words.
So, take a deep breath, and let's dive into the world of oxygen and its impact on your body's fat-burning potential.
What is the Role of Oxygen in Weight Loss?
Oxygen plays an important role in weight loss by helping the body convert stored fat into energy, a process known as oxidation. Another popular theory is that fat is converted into carbon dioxide and water. In each case, one thing is certain: when breathing deeply, you burn more calories and reduce body fat more efficiently.
Of course, the fat-burning process can be further supported by regular physical activity and a proper diet. This is something we preach in our articles about effective approaches to losing weight.
Does Oxygen Intake Affect Metabolism?
Yes, oxygen intake significantly impacts metabolism by improving the conversion of nutrients into energy, which is essential for maintaining a healthy body weight. When you breathe in more oxygen, it not only enhances your body's ability to burn calories but also supports overall energy levels.
During our research, we also discovered that insufficient oxygen can limit metabolic rates, especially during intense activity. And this causes a decrease in energy production.
But What is the Source of Energy for Muscles?
Muscles get their energy from a molecule called ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate). ATP is produced during the conversion of nutrients with the help of oxygen. The more oxygen you take in, the more efficiently your body can generate ATP, providing the needed energy.
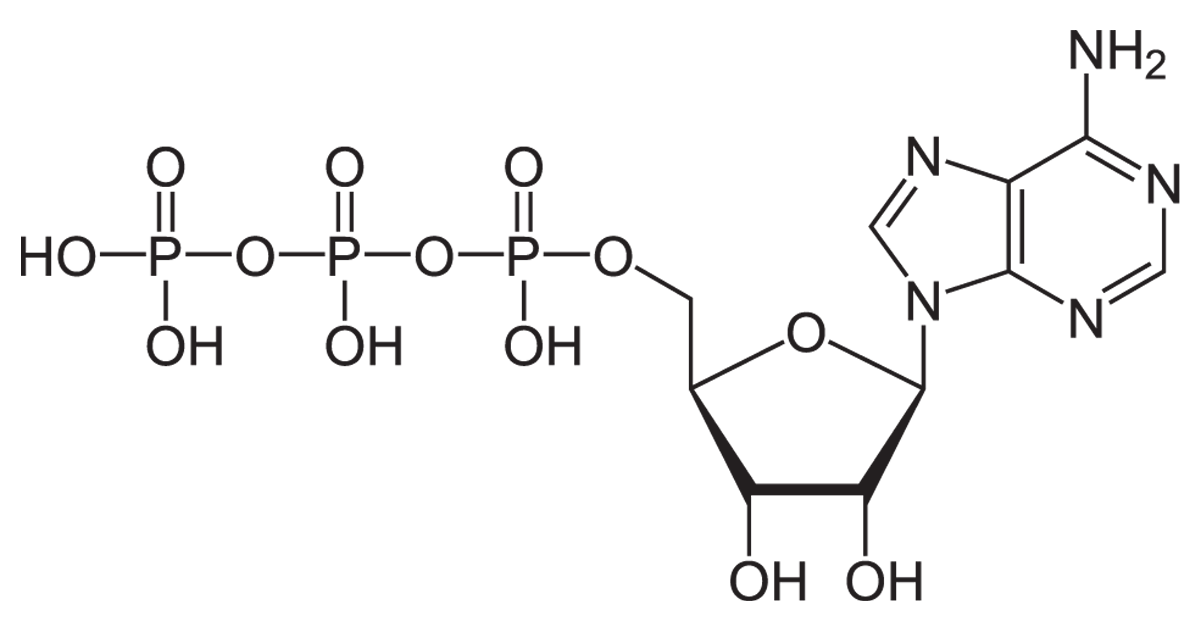
What is ATP in a Simple Definition?
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is like a battery that powers our muscles and helps us move and do things. Your body creates ATP by breaking down the food you eat every day, and this energy fuels all your physical activities.
We must also note that ATP stimulates the thermogenesis process. When ATP is used for energy, it generates heat. This helps maintain body temperature and increases your metabolic rate, leading to more calories burned.
Read this article to see all options to boost metabolism for weight loss.
The Connection Between ATP and Oxygen
We'll illustrate the link by a real-life example. Let's say you start lifting weights.
For the first four minutes of your workout, your muscles feed off the ATP energy in your muscle fibers. Once the stored energy is depleted, the muscle cells combine Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP) and Creatine Phosphate (CP) to produce 25 to 30 seconds of ATP energy.
To keep things simple, we'll only mention that ADP and CP are molecules that generate ATP. If you want to learn more about the process, check out this document from eScholarship.
Continuing from where we left off, your muscles have about 30 seconds of ATP energy available.
Once that energy is gone, your body has to use glycogen (blood sugar). Your muscles break down glycogen to produce ATP energy again.
And that's when oxygen comes into play…without oxygen, more energy can't be made.
How Does Breathing Faster Help You Burn More Fat?
So far, we know that your body produces energy thanks to oxygen and glycogen. However, the human body has only 400 to 500 calories of glycogen.
As glycogen supplies run low, your body turns to fatty acids as an alternative form of energy. It activates the fat cells stored for this occasion to fuel your body. The more oxygen present in your blood during a workout, the more fatty acids you can torch.
And that's how faster, deeper breathing instigates fat loss.
It doesn't matter whether you prefer the theory that fat is burned as energy or it leaves the body through your lungs. Either way, the magic happens when you work out.
There has been a buzz about breathing techniques that can potentially help you lose weight. Such exercises may manage stress levels or promote good health.
But we believe you'd agree that…
Sitting and breathing can't be more effective than pushing yourself in the gym or doing any form of intense physical activity when trying to shed some pounds.
And if you want to take it to the next level…check out our top-rated product.
We designed SKALD to help folks like you achieve weight loss goals faster in an unharmful way. It elevates your mood and blood oxygen levels, gives you more energy, and curbs your appetite.